- (91) 7972-978-204
- info@fatcoder.com
- Pimpri-Chinchwad
VBA Terms (Editor)
You will become familiar with the terms that are frequently used in Excel VBA. Understanding each of these terms is important because they will be utilised in upcoming modules.
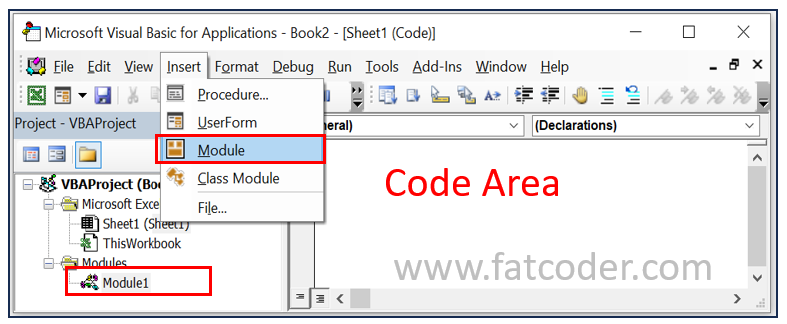
2. Module-Level VBA:
| Feature | Sheet-Level VBA | Module-Level VBA |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Global to the workbook | Specific to a sheet |
| Organization | Less organized | More organized |
| Reusability | Limited reusability | High reusability |
| Complexity | Suitable for simple tasks | Suitable for complex tasks |
Syntax:
Sub ProcedureName()
' Your code here
End SubSub: Keyword to declare a procedure.ProcedureName: A unique name for the procedure.(): Parentheses to enclose parameters (optional).Your code here: The actual code to be executed.End Sub: Keyword to mark the end of the procedure.
Example
Sub ProcedureName()
' Your code here
msgbox("Hello World")
End Sub
Methods are collections of statements that are run together to tell Excel how to carry out a certain task. Either a very basic or a very complex task may be completed. However, it is a good idea to breakdown complicated methods into simpler ones.
The two types of Methods are Sub and Function.
Functions and sub-procedures operate similarly. Functions may or may not return a value, but sub-procedures does not return a value.
It is possible to call subroutines without using the call keyword.
In Sub and End Sub statements, sub procedures are always enclosed.
A collection of reusable code that can be called from anywhere in your program is known as a function. This removes the necessity of repeatedly writing the same code. Programmers can use this to break up a large program into several parts that are simpler to handle.
In addition to built-in functions, VBA also enables the writing of user-defined functions and the writing of statements between functions and end functions.